
Quiz Summary
0 of 15 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- Current
- Review / Skip
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 15
1. Question
A 27-year-old male requires intubation and ventilation for life threatening asthma. He has been given an induction agent and neuro-muscular blockade. An attempt to intubate him fails, because of a limited view as the larynx could not be seen. Ventilation with a bag and mask was resumed, maintaining an acceptable oxygenation. At this point a more experienced intubator arrives
Which of the following is the best strategy now?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 15
2. Question
An 82-year-old woman presents after a fall at home. She tripped in the hall while answering the doorbell and has only a small hip bruise.
Her past medical history includes osteoarthritis, hypertension, and insomnia. Her regular medications are:
- Amlodipine 10 mg once daily
- Paracetamol 1 g four times daily
- Diazepam 5 mg at night
- Omeprazole 20 mg once daily
She mobilises independently and lives alone. Her ECG and blood tests are normal.
Her blood pressure is 144/82 mmHg, with no postural drop.According to NICE guidance on falls prevention, which intervention is most appropriate before discharge?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 15
3. Question
You are asked to give your opinion on a CT image of an 11 year old child who is being managed by the paediatric department with a three-day history of difficulty swallowing. The child has become progressively more unwell and is now febrile, in significant pain and drooling saliva. A contrast enhanced CT has been undertaken and the staff are studying this image:
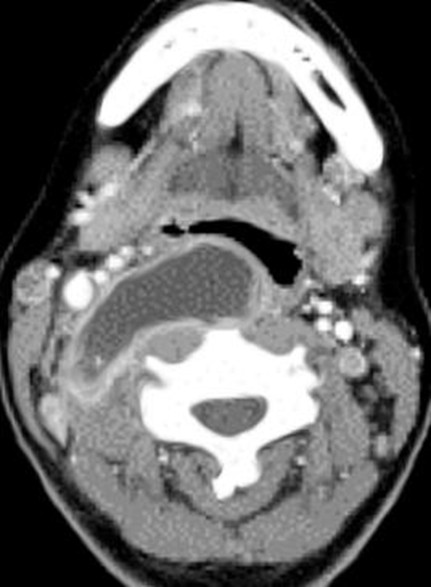
What is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 15
4. Question
A study was described as a randomised controlled trial investigating the effect of a new treatment for ureteric colic. The primary outcome was reduction in pain score. The intervention group (new drug) was made up of patients whom clinicians felt required stronger analgesia, while the control group received standard treatment according to national guidelines.
Which form of bias is most likely in this study?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 15
5. Question
A 12-year-old boy sustains a displaced distal third fracture of the right radius and ulna (≈20° angulation) after a fall. The ED and orthopaedic teams recommend closed reduction (and possibly internal fixation if adequate alignment cannot be achieved). However after analgesia, he is comfortable in a sling; and he and his parents refuse reduction, stating “it will heal on its own.” Two senior clinicians have explained the risks of malunion and functional loss, but refusal persists.
What is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 15
6. Question
A 78-year-old woman with known dementia is brought to the Emergency Department by ambulance after being found unresponsive at home. On arrival, she is awake but extremely agitated and combative, yelling and pushing away anyone who approaches. The ambulance crew report that her blood glucose level was 1.8 mmol/L. She refuses to let anyone take a blood sample or insert a cannula.
Which of the following is the most appropriate first step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 15
7. Question
In a randomised controlled trial (RCT) comparing two asthma inhalers, some patients in both groups stopped using their assigned treatments. However, the results were still analysed based on the original group allocation.
What type of analysis is this?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 15
8. Question
A 46-year-old woman presents with a sudden, severe headache. She undergoes a CT head scan 12 hours after the onset of symptoms. The sensitivity of CT for subarachnoid haemorrhage falls after 6 hours, but the specificity remains very high (close to 100%).
What does the high specificity indicate?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 15
9. Question
A test for subarachnoid haemorrhage has a sensitivity of 98% and a specificity of 65%.
What does this high sensitivity indicate in practice?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 15
10. Question
You are called to the observation ward (CDU) where a 19 year old male is causing a disturbance. He is heavily intoxicated and has taken an overdose of a large amount of paracetamol, requiring treatment with acetylcysteine. However he does not want to complete the treatment and instead wants to leave the hospital.
What is the most appropriate next action?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 15
11. Question
The emergency department is crowded. A combative patient was unloaded by the ambulance crew to a trolley. As there was no cubicle available the trolley remained in a quiet corridor. About 30 minutes later the patient was found to be unresponsive and attempts at resuscitation were unsuccessful. The family have been contacted.
Which of the following strategies would be most appropriate after this incident?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 15
12. Question
A team is studying whether a new scoring system predicts sepsis in ED patients. They prospectively collect data from 500 patients and follow them for 28 days to see who develops organ failure.
What is the best description of this study design?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 15
13. Question
A trial finds that a new drug reduces systolic blood pressure by 10 mmHg, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 5–15 mmHg.
What is the correct interpretation of this confidence interval?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 15
14. Question
A junior colleague has asked for your help interpreting an x-ray. A 71-year-old man has a sharp sensation of something stuck in his throat after eating fish and chips a few hours earlier. He is concerned about a fishbone. He has swallowed water and dry bread to try to clear his throat, but this has not resolved his symptoms. This is the x-ray:
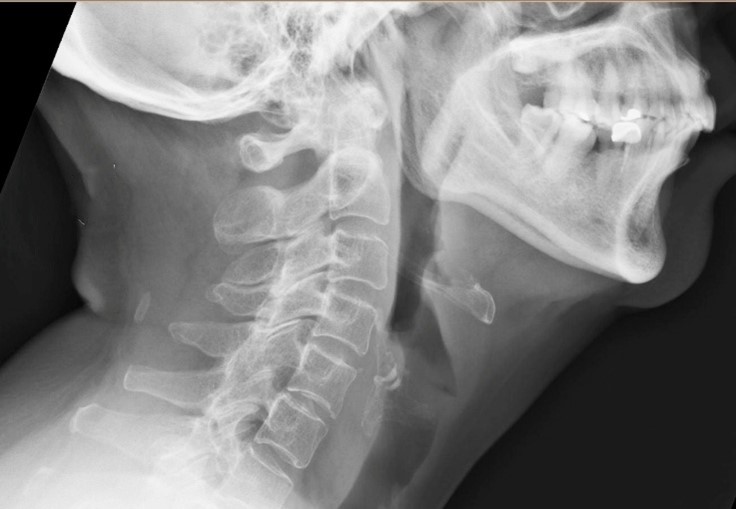
What would be the most appropriate advice?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 15
15. Question
A 15-year-old girl presents to the ED with lower abdominal pain, accompanied by her mother. A nurse tells you the mother wishes to be present during the consultation.
What is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect

